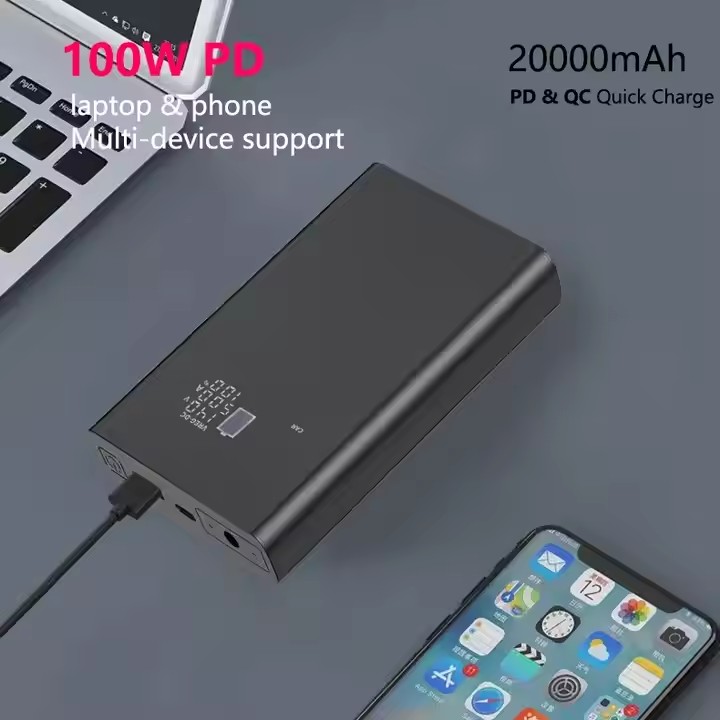
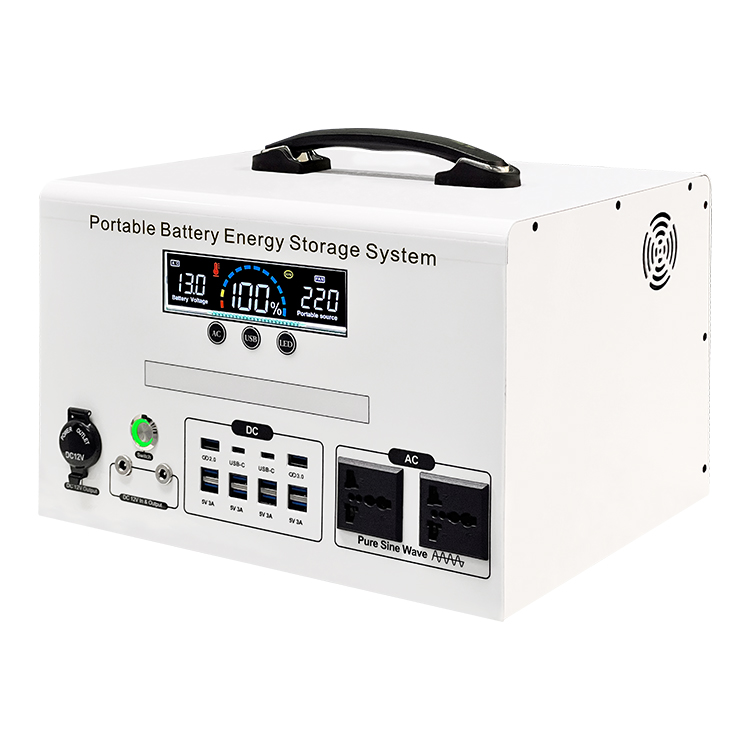
YX-DC12
PD 100W DC Powerbank 20000mah 9V 12V 15V 16.5V 19V 1A 2A 3A 4A 5A 6A Laptop Power Bank 24V 20V for CPAP Router Projector Modem

YX-CDB-1034
15000mAh Power Bank External Battery PowerBank with Magnet+Wireless+Powerbank+Charger+cable+Powerbank
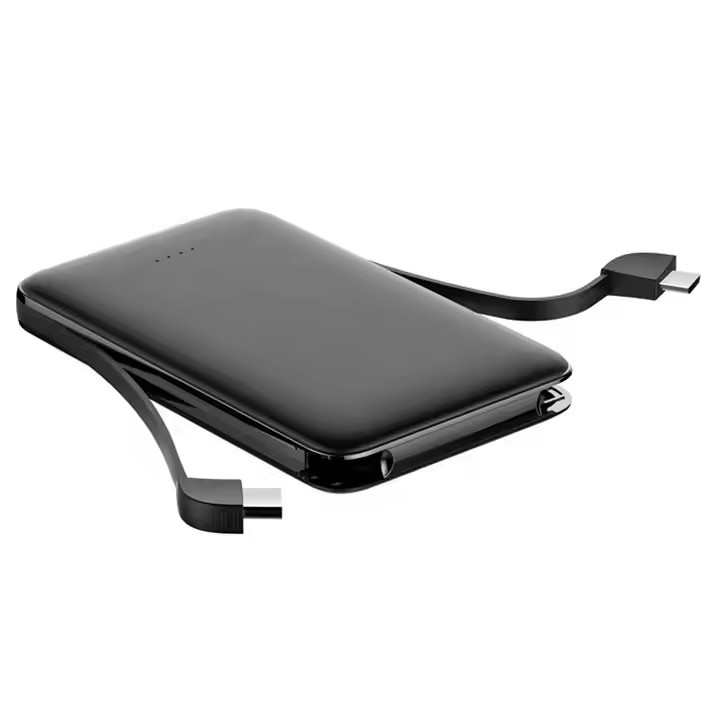

YX-YFT-P07
High Quality Portable Power Banks Built-In Dual Cable Slim Oem Led Display Quick Charging Powerbank 5000mah 10000mah
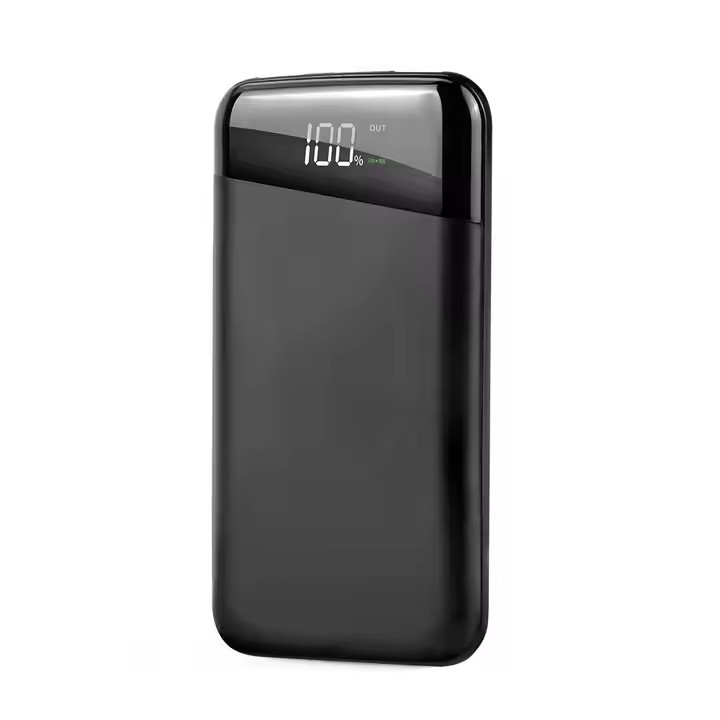

YX-AA-P1025
Hot Sale10000Mah Slim Power Bank With Led Digital Display Hot Sale Portable Wireless Charger Power Bank

YX-PB0077
Hot Sale 10000mAh Mini Power Bank High Lithium Portable Charger Digital Display Compatibility iPhone Micro Type-C Devices

YX-CD150
USAMS CD150 Slim USB Power Banks Fast Charging 10000mAh Mobile Charger Power Banks with Lanyard LED Display
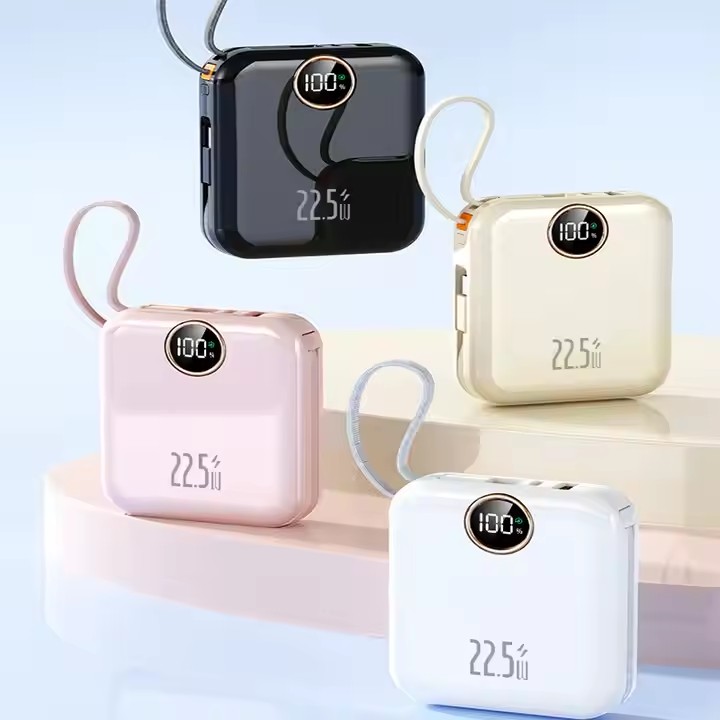

YX-PRC-DX347
Super Charging PD22.5W Outdoor Portable Power Bank High Capacity Charger Built in Cable with LED Digital Display for iPhone