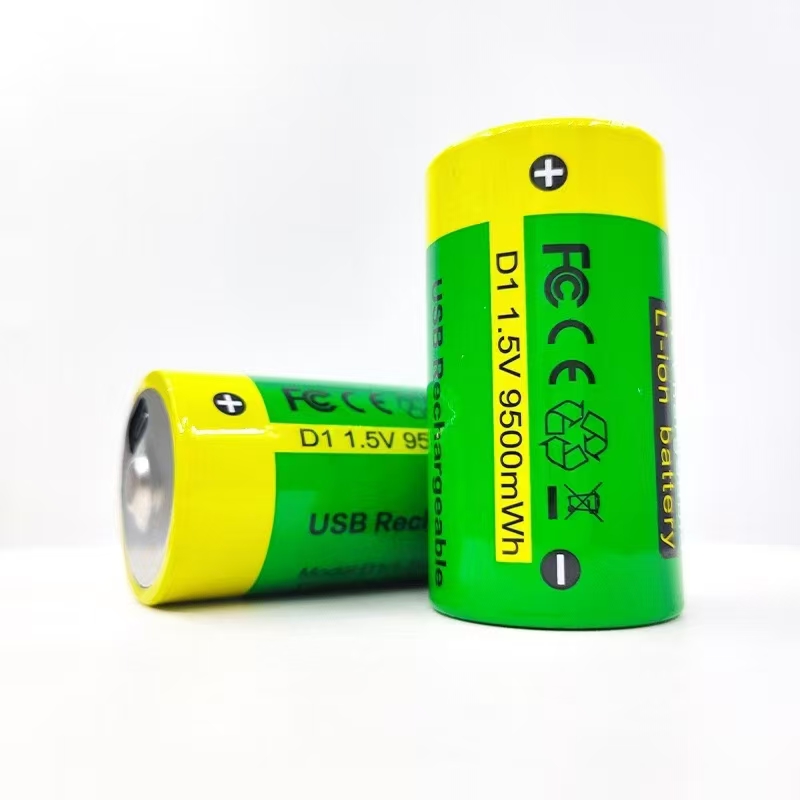
YX-D-1.5V 9500mWh
Intelligent Conversion, Convenient Life: 1.5V Lithium Battery to Dry Battery Converter, Plug and Play, Easy Upgrade
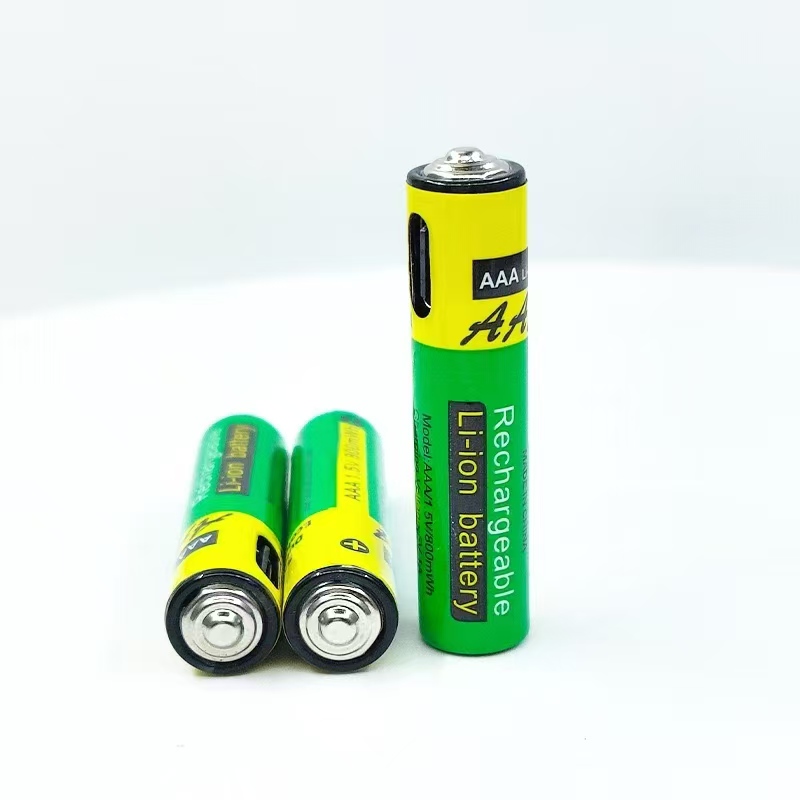

YX-AAA 1.5V 800mWh
Intelligent Conversion, Convenient Life: 1.5V Lithium Battery to Dry Battery Converter, Plug and Play, Easy Upgrade
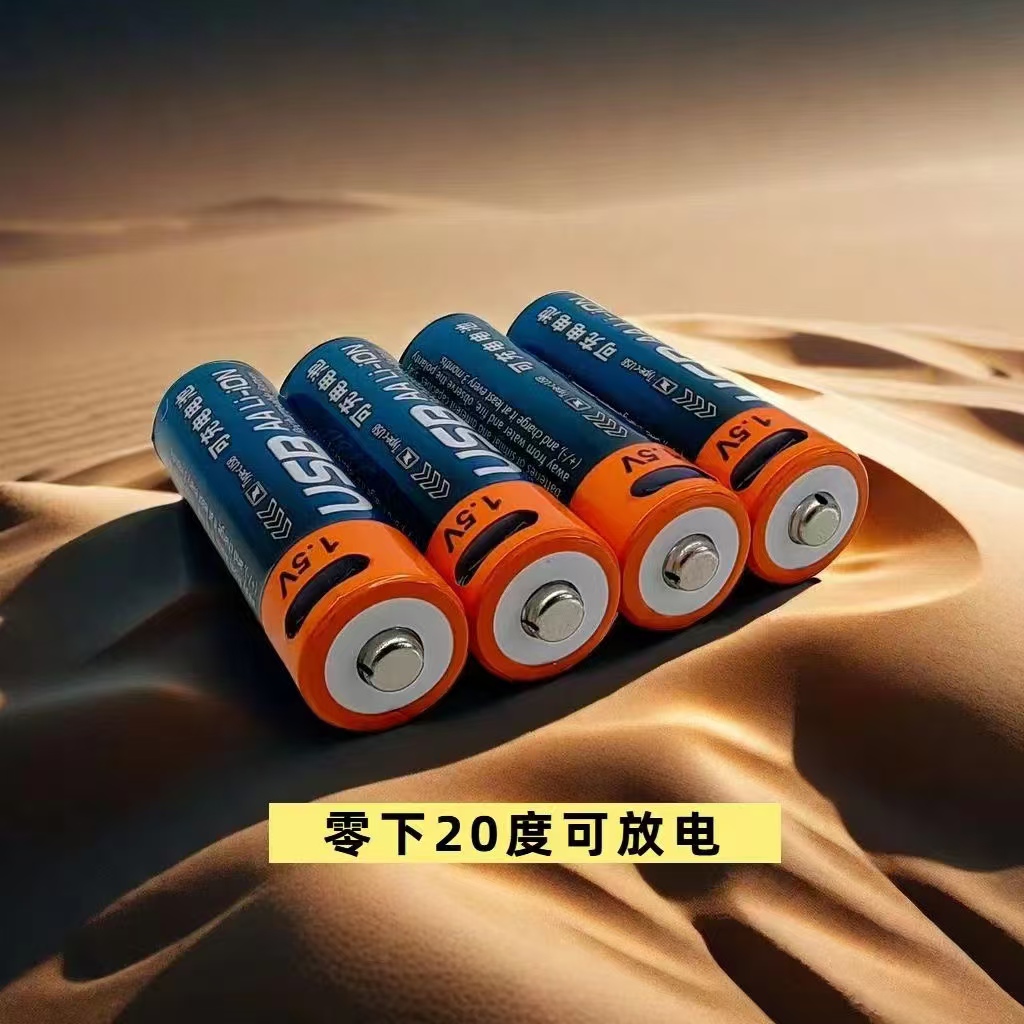

YX-AA 1.5V 2800mWh
Intelligent Conversion, Convenient Life: 1.5V Lithium Battery to Dry Battery Converter, Plug and Play, Easy Upgrade
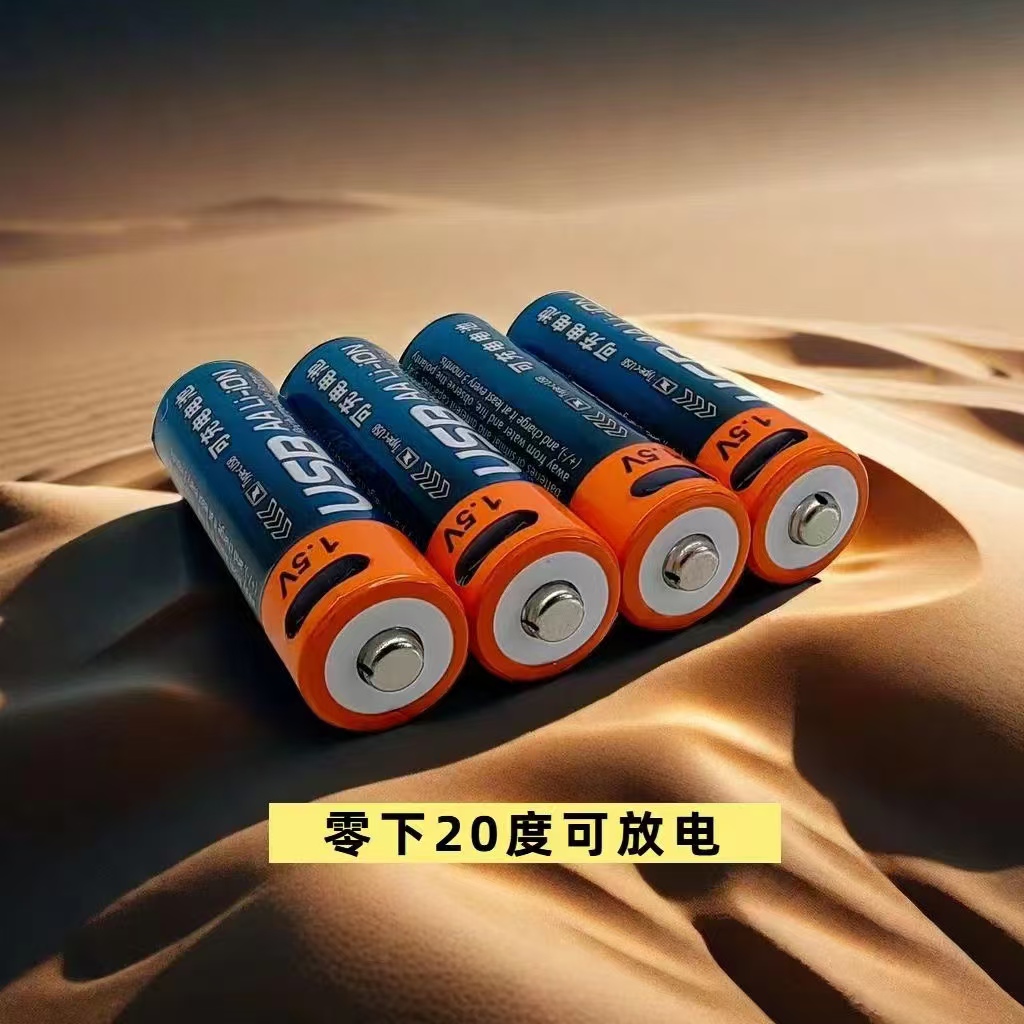

YX-AA 1.5V 2400mW
Intelligent Conversion, Convenient Life: 1.5V Lithium Battery to Dry Battery Converter, Plug and Play, Easy Upgrade
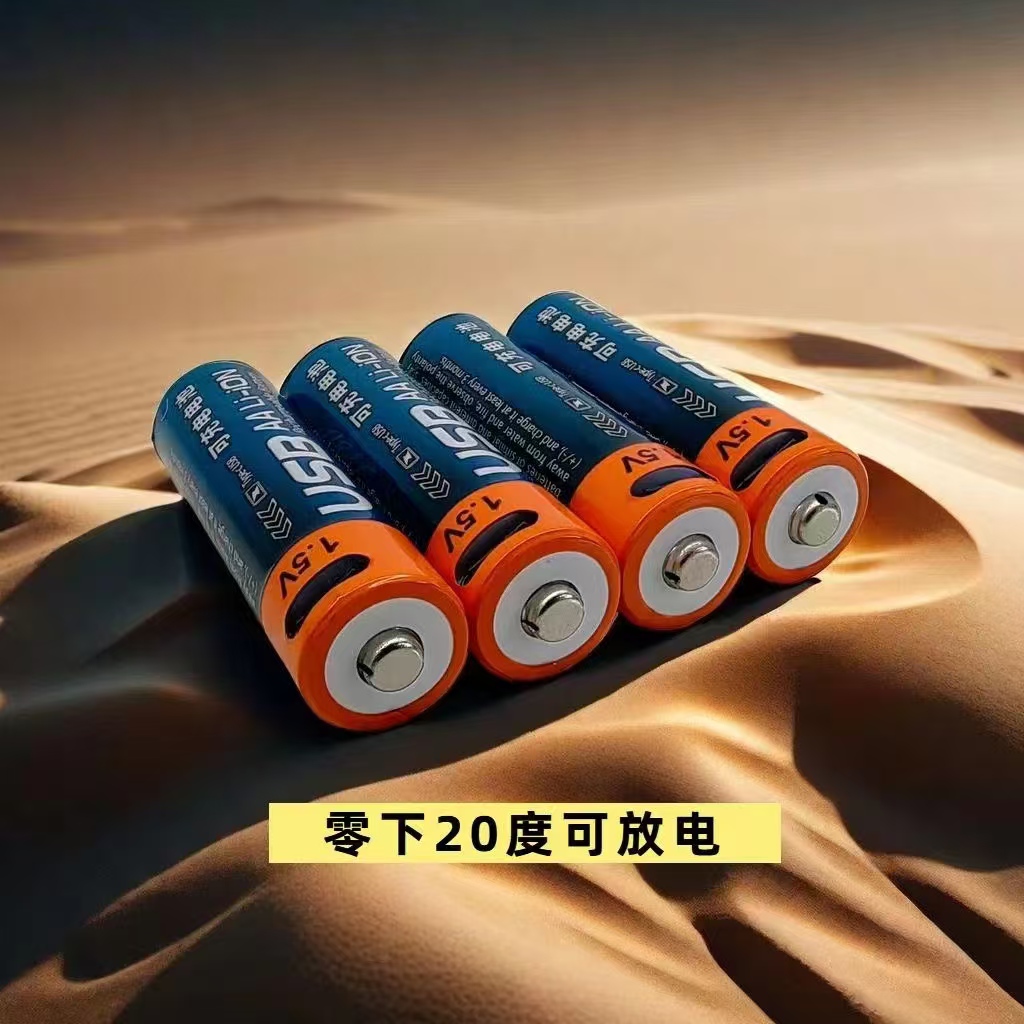

YX-AA 1.5V 1480mWh
Intelligent Conversion, Convenient Life: 1.5V Lithium Battery to Dry Battery Converter, Plug and Play, Easy Upgrade
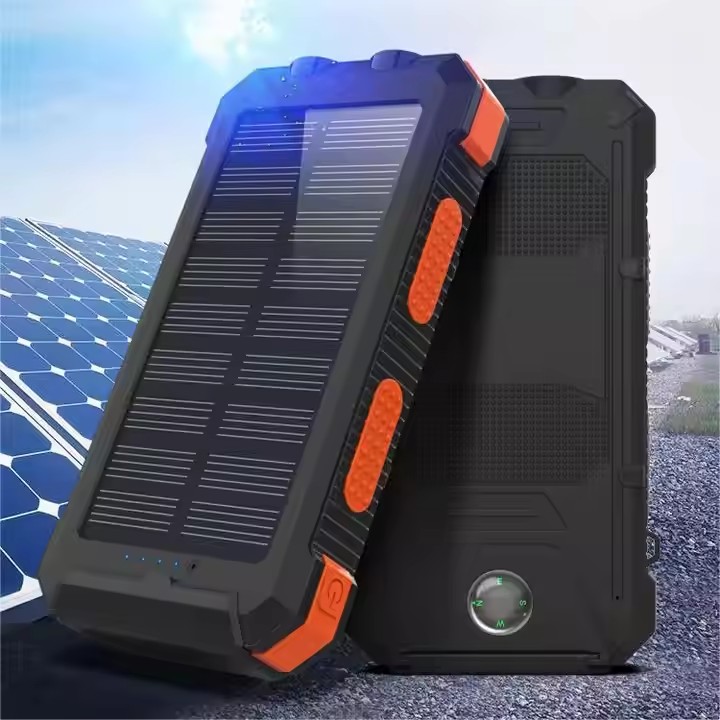

YX-1602B
New foldable waterproof and shockproof 20000 mAh fast charging solar panel charge outdoor portable solar power bank
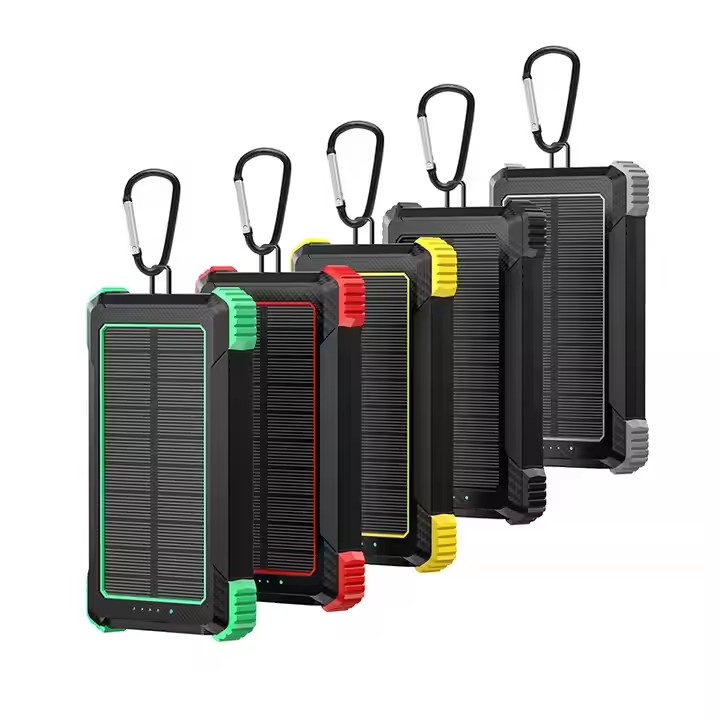

YX-803
High quality wireless charging power bank, dual USB waterproof solar power bank with lighting, can be customized logo
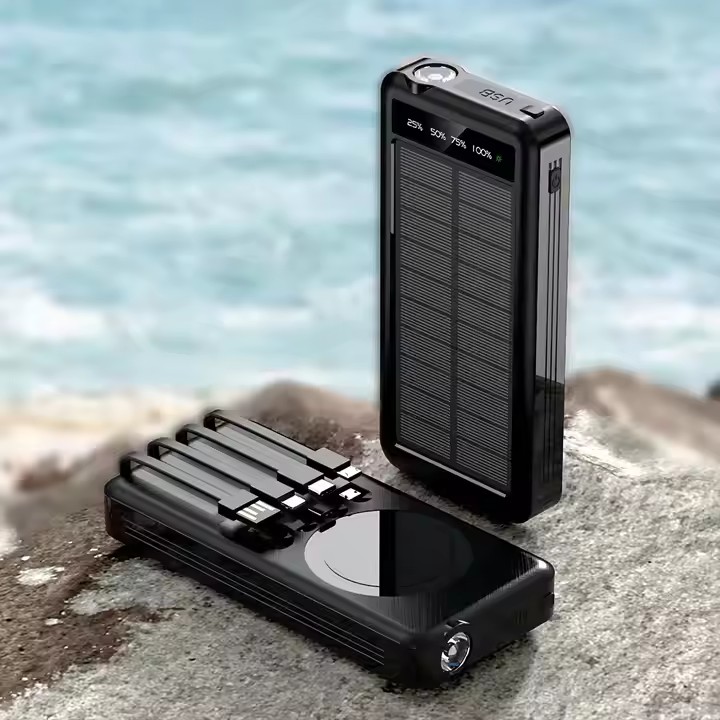

YX-809
Portable 10000mAh large capacity built-in cable powerbank with flashlight solar wireless charging can be customized mobilepowe
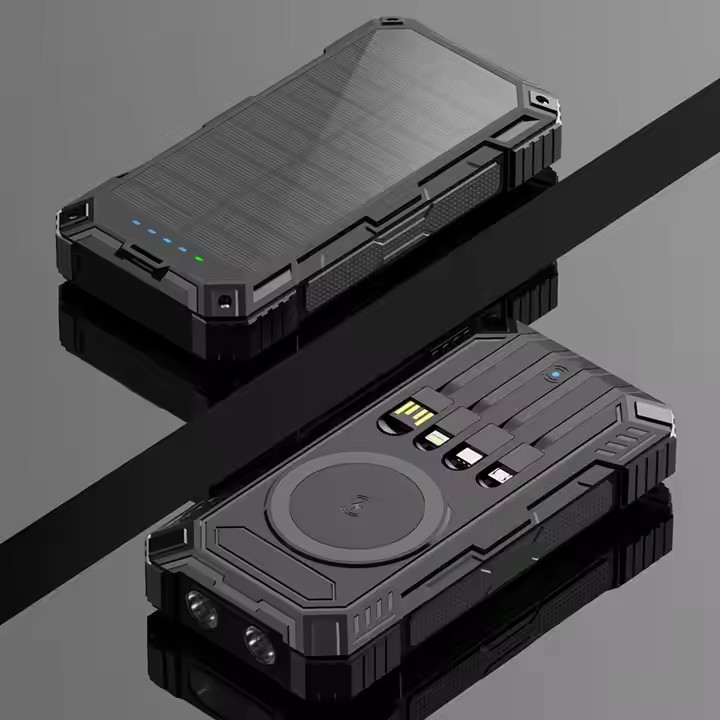

YX-902
Portable Built-in Cable Super Fast Charge 15W Wireless Fast Charging Solar Power Bank For Outdoor Use
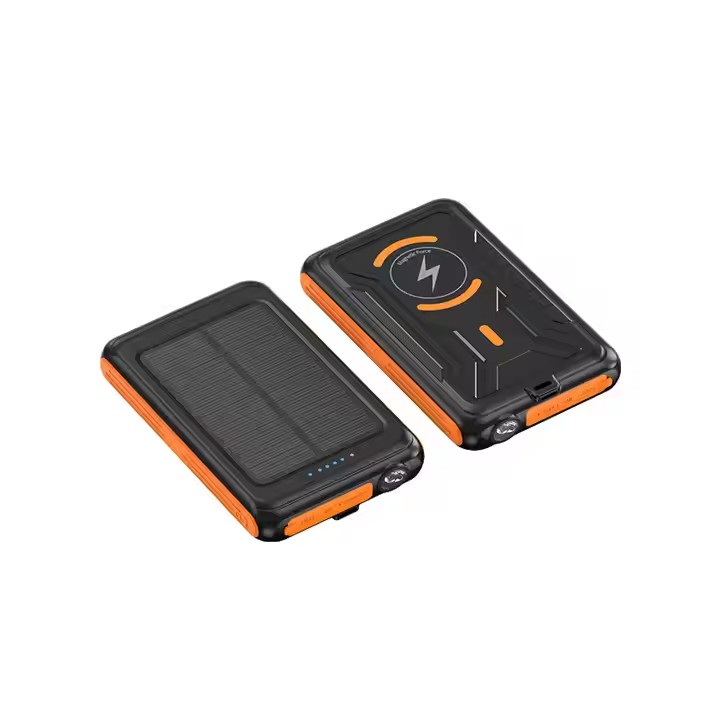

YX-808
New Portable Solar Charger 5000mAh Magnetic Wireless Charger Power Bank For Cell Phone Tablet
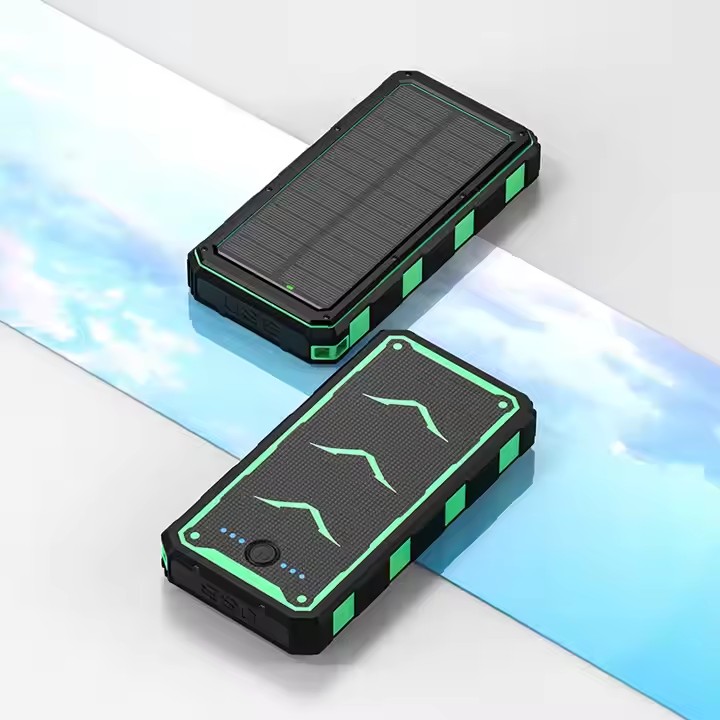

YX-802
Warframe solar powerbank 20000 mah large capacity PD fast charge wireless charging treasure factory direct sales
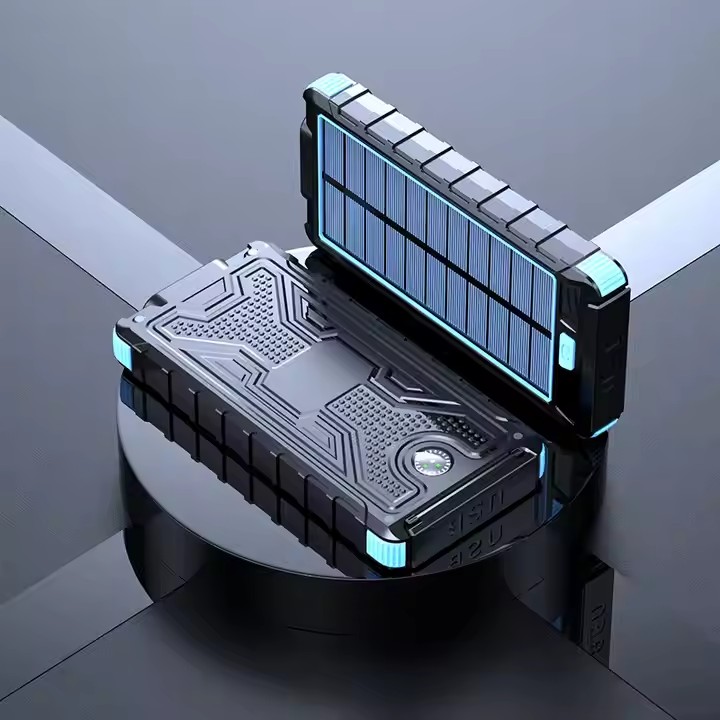

YX-801
Factory Direct Sale 10000mah Drop-Proof Solar Charging Treasure Super Fast Charging Power Bank For Cell Smartphones

YX-2101B
New Triple Defense Folding Bag Solar Power Bank 3A Fast Charging Self-contained 4-wire Lighting Wireless Charging Power Bank
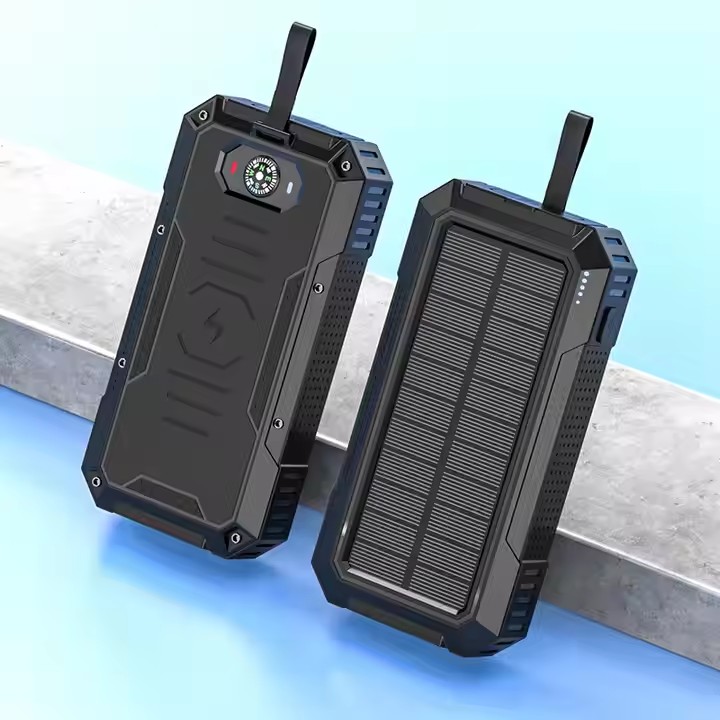

YX-804
Solar Power Bank Wireless Outdoor Mobile Power Cross-border Hot Selling Product Waterproof PD22.5W Fast Charge 30000 Mah ABS,PVC
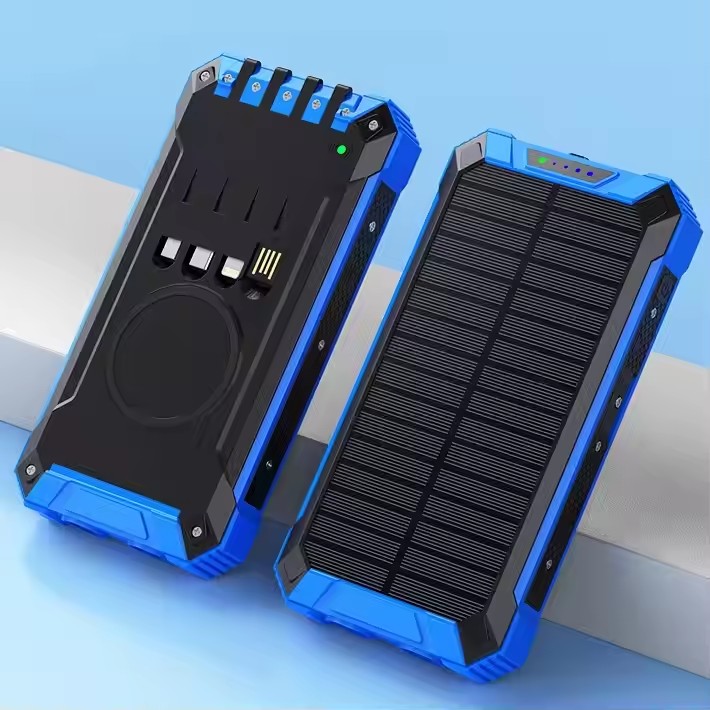

YX-2101A
New solar power 20000mAh large capacity 10W wireless charging power bank comes with charging cable ,fast charging power bank
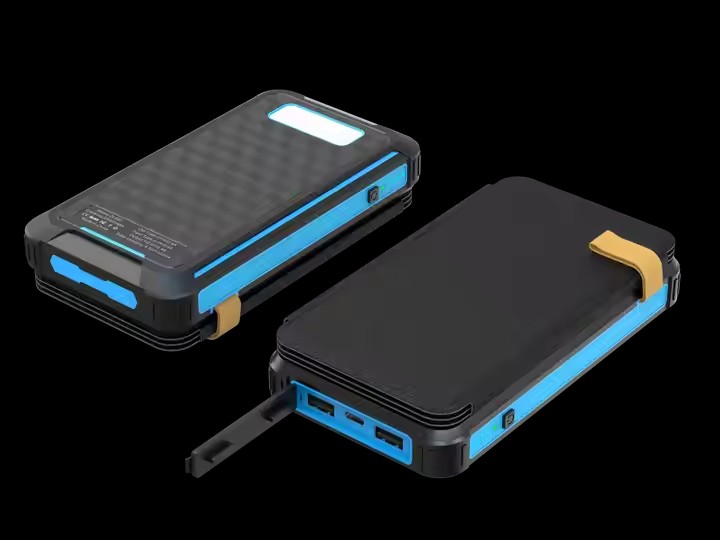

YX-900
New Multi-USB Output Solar mobile power 20000mAh High Power Solar Folding with Lanyard Design Power Bank
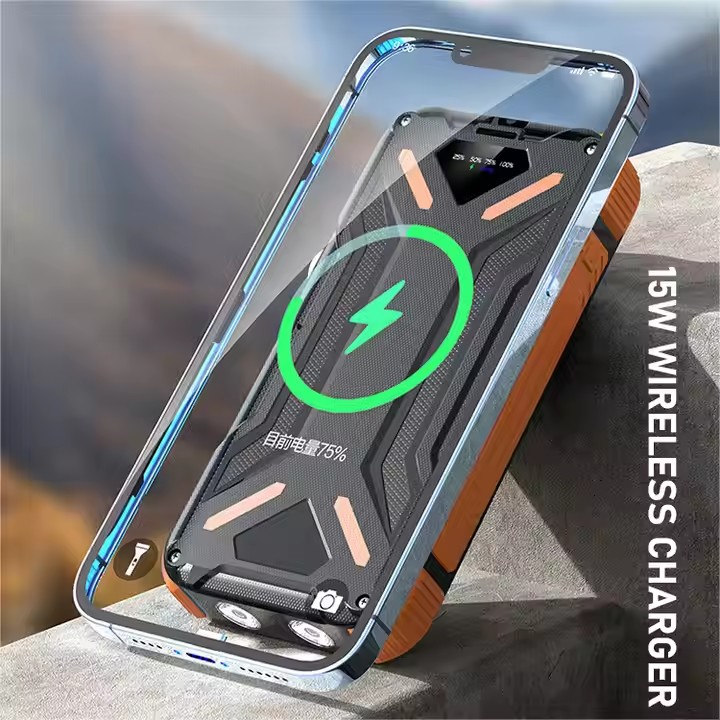

YX-807
New 20000mAh Large Capacity Drop-proof Multifuncional Solar Charger Power Bank For cell phone

YX-806
Outdoor Camping Wireless Fast Charge 20000 mAh Large Capacity Charging Treasure Solar Three-proof Design Mobile Power